ATROPHIC SCARS treatment and correction
In the treatment of atrophic scars there is no universal method for removing acne scars or scars after accidents. You can not completely remove a scar and acne scar, but it is possible to improve scars significantly with different methods. Different types of atrophic scars have different reactions in response to different treatment methods.
That is why a very important first step in the treatment of scars and acne scars is the definition of the type of scar. For example ice pick scars are best treated with chemical peels such as TCA cross or punch excision. Rolling scars are best treated with microdermabrasion, microneedling (dermaroller, dermapen), fractional laser (Fraxel) and subscision. Boxcar scars answer satisfactory to treatment with carbon dioxide laser.
For the treatment of atrophic scars are whole palette of capabilities and techniques.
Microdermabrasion – skin polishing of the scar localization with aluminum oxide microcrystals (Al2O3).
Aluminum sand is applied onto the skin surface by means of negative pressure and, knocking the particles out of the problem zone, aluminum sand is sucked into another container. Vacuum enables to elevate the scar bottom (Fig.1). This method does not require anesthesia, the recovery period being 4-10 days. To archive tangible results, 3-5 procedures are required with a 3-4 week interval (Video: Microdermabrasion of the fresh scar before after with Dr. Igor Safonov).
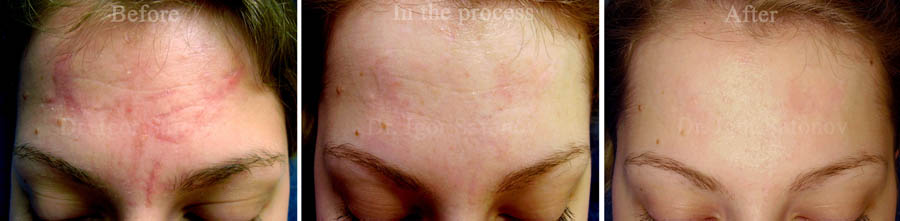
Fig.1. Microdermabrasion of atrophic scar
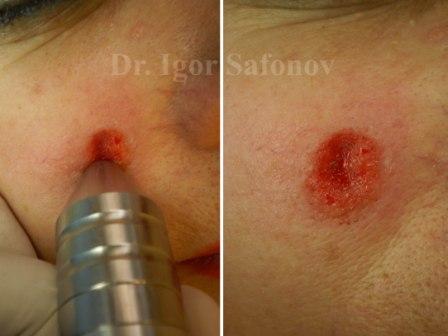
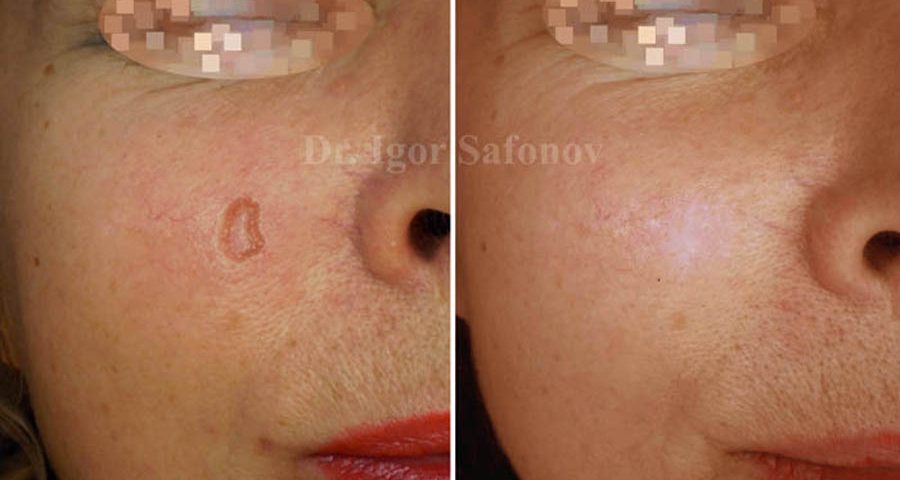
Fig.2. Atrophic scar before and after microdermabrasion
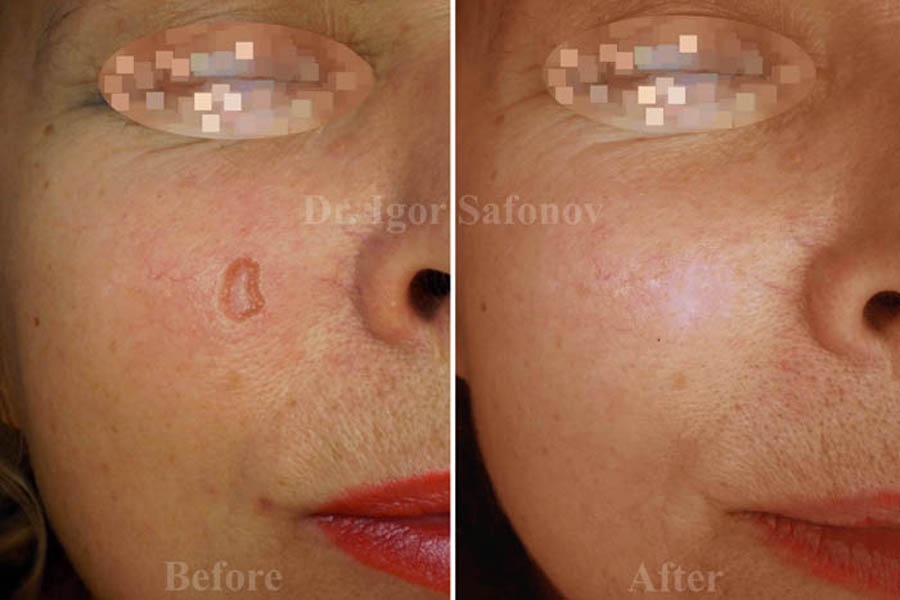
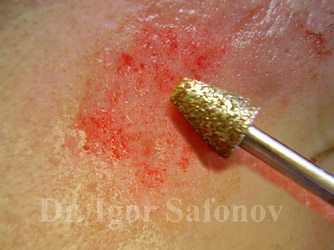
Fig.3. Deep rotational dermabrasion. Blood dew
Deep rotational dermabrasion. Surgical dermabrasion with rotational discs was first described by Kromayer in 1905. Abrasive fraises with 20 000 – 60 000 r / min were introduced in the 60`s of the last century (Fig.3). This device used Dr. Igor Safonov for atrophic scars treatment, as well as for correction of hypertrophic scars, but not for the correction of active keloids. Papillary derma layer is the application point. The fraise does not remove the scar tissue alone, but as well as the adjacent normal skin.
Fig.4. Atrophic scars before and after deep rotational dermabrasion
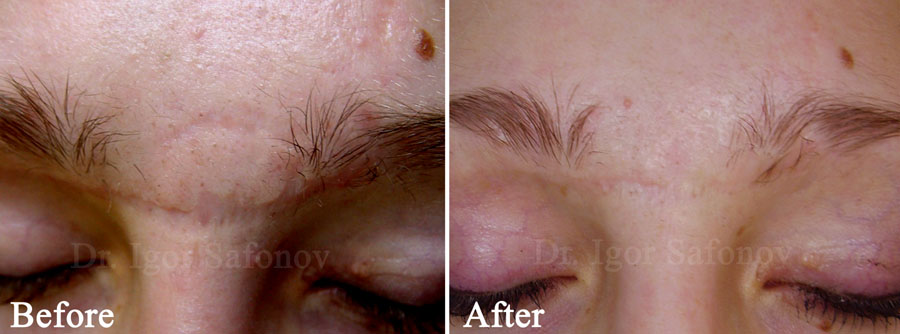
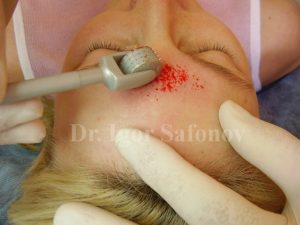
Fig.5. Collagen Induction Therapy or microneedling
Collagen Induction Therapy or microneedling. The application of dermaroller (Fig.5) forms hundreds of microscopic channels in the skin. Following a number of complicated consecutive reactions (hemostasis – inflammation – proliferation – remodeling), fibroblasts, special skin cells, “patch” the microscopic channels formed by dermaroller needles. Collagen islands are synthesized within the channels, which are attracted to one another, thus gradually aligning the edges of scars or striae. In this manner an elastic backing of fresh collagen tissue is created on the one hand, decreasing the width of scars/striae by retracting and elevating their bottom to the skin surface on the other hand (Fig.6). (Scar treatment with microneedling (Dermapen / Dermaroller) shows Dr. Igor Safonov in this video)
Fig.6. Microneedling for acne scars before and after. Treatment with Dermaroller
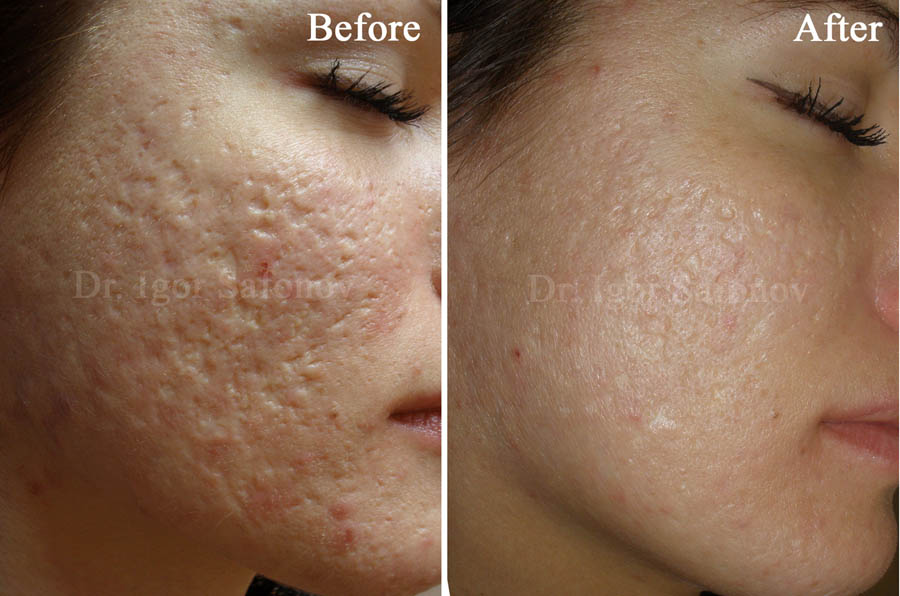
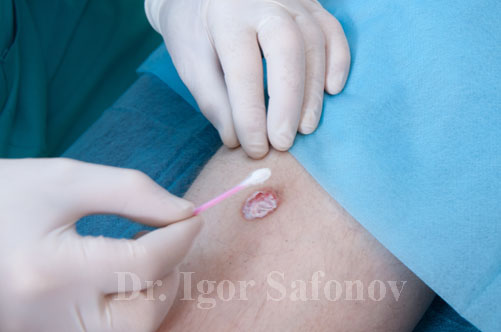
Fig.7. Topical therapy for atrophic scars
Creams and gels for scars treatment. Different ointments, creams and gels are applied depending on the stage of scar formation, such being antibacterial, normalizing blood circulation, reducing or stimulating collagen synthesis, diluting wound environment, boosting immunity of the wound area, etc. To this end Kelo-cote, Dermatix, Strataderm, MedGel, Kelofibrase, Scarguard, Contractubex, Aldara. But there is a scars treatment cream that stands out among others. It called Elicina and consists of 80% of the snail mucus extract. This cream accelerates the regeneration process and can change the structure of scar tissue. Therefore Elicina snail cream can be apply for all types of scars: atrophic and hypertrophic after injuries and ugly scars after surgery. Each individual case surely requires a consultation with the attending physician to select the necessary cream, ointment or gel, because silicone based products can not improve, but can worsen the condition of the atrophic scar. Topical therapy is usually applied either in parallel to, or after mechanical treatment methods (Fig.7)
Subcision. This method was developed by David S. Orentreich, Dermatologist. (Fig.8).
Fig.8. Subcision. Scheme
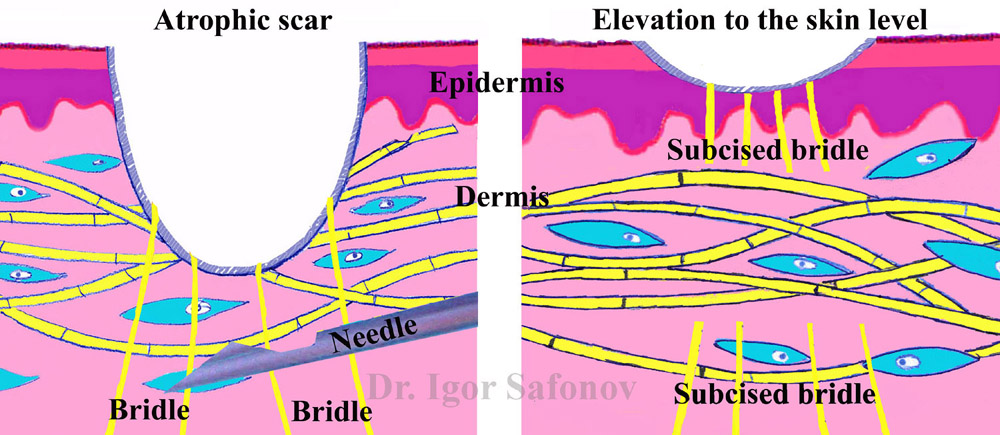
The principal of this method is as follows. The process of scar maturation is accompanied by the development of connective tissues that fixate the scar bottom embedding it into derma. Connective bridles are subcised by the needle and the released scar bottom elevates. The defect aligns (Fig.9). Subcision shows best results for rolling scars.
Mesotherapy. Mesotherapy in its broad context is the injection of cosmeceutical and pharmacological drugs into the middle layers of skin (mesoderm) to improve the scar appearance, whereby primarily using the so-called fillers (filling agents). Fillers can be natural, synthetic and semisynthetic. Apart from fillers, fibroblasts are injected (those being cells, synthesizing collagen), a variety of microelements stimulating the healing of wound and scar formation, different enzymes, etc.
Laser treatment for atrophic scars and acne scars. Many physicians in clinics will “by default” prescribea laser treatment such as fractional laser (Fraxel), Erbium Laser, Smoothbeam etc. Whilst these lasers can give some results, they are not Gold Standard for acne scar treating. Ablative and non-ablative lasers are used in atrophic scar correction. Carbonate (ablative) laser vaporizes upper skin layers or burns microchannels through the skin (Fig.10), where fibrous lesions being formed thereafter. The skin relief is flattened due to the formation of multiple collagen and fibrous areas. Treatement with Carbon dioxide laser may cause complications (lasting redness, pigmentation, transformation of atrophic scar into keloid).
Fig.10. Atrophic acne scars treatment with Fraxel ablative laser
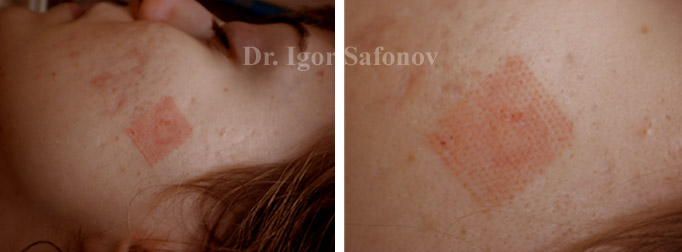
Fig.11. Laser facial scar removal before and after. Atrophic scar treatment with pulsed dye laser
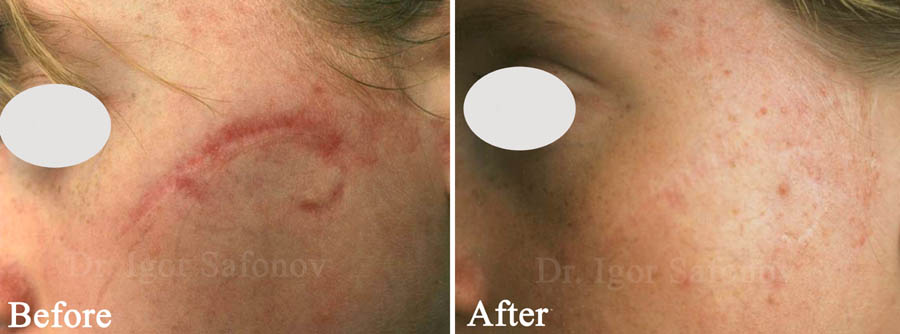
Vascular (non-ablative) laser simply glutinates the vessels within the scar (Fig.11). As a rule, vascular laser treatment is not followed by any complications.
Chemical peeling for scars and acne scars. Peeling incorporates the notions “to purify”, “remove the skin” and “exfoliate”. Therefore, any exfoliation-related process of epidermis in the upper layers of derma is basically referred to as a peeling. Depending on depth of effect, all peelings are divided as follows:
- superficial – several layers of keratinized cells;
- middle – throughout keratinized layer;
- deep – throughout epidermis down to the basal layer and papilla dermis, penetrating into reticular dermis.
Fig.12. Scratches and small scars before and after series of middle peeling
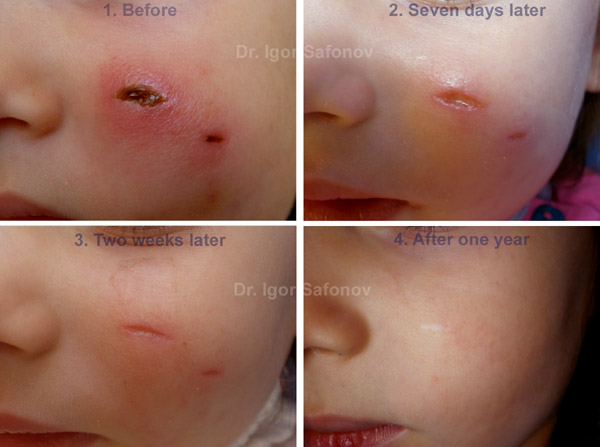
Dr. Igor Safonov recommends for scar treatment and as a cosmetic treatment against scar tissue formation such procedures: massage, lymphatic drainage, skin moisturization. As a result of injury or inflammation of dermis, occasionally in subcutaneous fat, edema is being formed. It is proven that the bigger the edema is, the cruder the scar will be. Therefore edema is to be treated within the first hours after injury and continued throughout the scar formation process. The second task is to ensure the flow of nutrients to the scar that is being formed and the efflux of cellular waste products. The said tasks are effected by massage treatments and lymphatic drainage (Fig.13)
Fig.13. Lymphatic drainage treatment in combination therapy of the fresh scar of the left cheek