STRETCH MARKS Treatment and Correction
The treatment of stretch marks is complicated by the fact that only fresh (red) stretch marks can be eliminated without a trace.
What are stretch marks?
Stretch marks are essentially a type of atrophic scar. They are formed due to various reasons like pregnancy, rapid dieting, long-term treatment with steroids, body growth during puberty, etc.
Why do you get stretch marks?
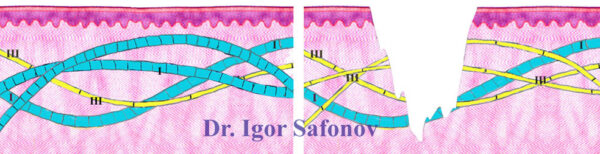
There are many causes of stretch marks, but they have one thing in common: disruption of collagen fibers or a significant decrease of collagen synthesis. Collagen fibers provide elasticity to the skin and are responsible for its strength and elasticity. More than 20 different types of collagen have been identified in the human body, but only two of them play an important role in the structure of the skin. They are collagen type I and collagen type III. They have a number of differences. Type III collagen fibers are more elastic and can stretch quite well. Type I collagen fibers are less elastic than Type III collagen fibers. Type I collagen fibers wear out faster when exposed to high stress. Type I collagen fibers are more likely to break down under high stress. If type III collagen fibers are predominant in the skin, no stretch marks are formed. If, on the other hand, type I collagen fibers predominate in the skin, stretch marks occur (Fig. 1). The percentage ratio of these two collagen types in a skin is genetically inherited. This means that if the mother or grandmother had stretch marks on the stomach or on the thighs, then it is likely that the daughter also has a high risk of getting stretch marks and not only on the stomach or on the thighs but anywhere on the body.
Risk factors (“predisposition”) to stretch mark appearance.
There are groups of people who are at greater risk than others of getting stretch marks:
overweight people
pregnant women
teenage girls at puberty age;
people with high-calorie diets;
people taking steroids
persons with frequent weight fluctuation;
genetic predisposition;
bodybuilders;
women in menopause.
Is it possible to get rid of stretch marks completely?
Today you can find many different remedies for stretch marks on the internet, such as anti-stretch mark cream, oil to prevent stretch marks, laser removal of stretch marks, etc. But nobody tells the truth that only red stretch marks (fresh stretch marks) are successfully treated. This period is between half a year and a year.
However, over time, the red stretch marks mature and turn white, known as white stretch marks or old stretch marks. White stretch marks are quite problematic to remove. Getting rid of white stretch marks at home is clearly impossible. Complete white stretch marks cannot be removed by laser as well as microneedling or any other methods like “stretch mark cream” or raw potatoes! But there are techniques that can make both red and white stretch marks almost invisible.
What method is the priority for stretch mark treatment?
The following methods are suitable for the treatment of red stretch marks on the abdomen, hips and buttocks: laser therapy, microneedling with a dermaroller or a dermapen, as well as carboxytherapy, creams, TCA peels, etc. However, an aggressive method such as laser treatment cannot be recommended for the treatment of stretch marks on breasts. This is because the breast area is very sensitive to the formation of keloids.
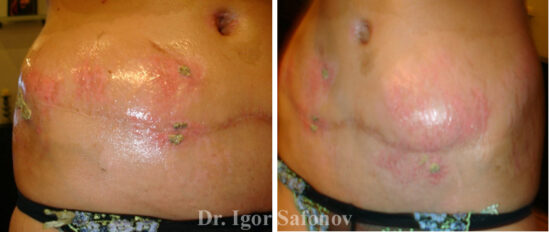
Removal of stretch marks on the abdomen with abdominoplasty
Abdominoplasty can be used as a surgical correction method to remove stretch marks on the abdomen. Abdominoplasty involves tightening the skin on the abdomen. When a strip of skin is removed, any stretch marks that were on it are also removed. However, any remaining stretch marks will be even wider due to the skin becoming taut. Therefore, abdominoplasty is not the method of choice for the removal of stretch marks on the abdomen (Fig.2).
Surgical excision of any stretch mark with intradermal suture is acceptable if the stretch mark is not wider than 0.5 mm. This is an expensive operation due to the delicate and careful work of the plastic surgeon. Additionally, it leads to a normotrophic scar formation in any case.
Treatment of stretch marks with mesotherapy
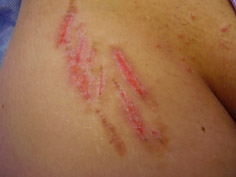
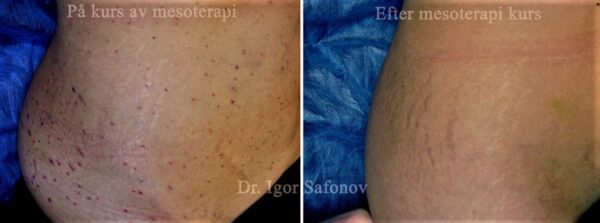
Mesotherapy is a method of delivering active substances and microelements to the dermis, the purpose of which is to improve metabolic processes in the skin. Mesotherapy is used to treat red stretch marks on the abdomen, hips, thighs and chest. It is quite painful to use this method for stretch marks on the buttocks and calves. Correction of white stretch marks (old stretch marks) with mesotherapy has no concrete results. Patients with long-standing stretch marks often abandon this method after 3-4 treatments due to the painful nature of treatment and lack of results (Fig.3)
Fig.3. Mesotherapy for old stretch marks on the hip and abdomen. Unsatisfactory results after treatment
Improving stretch marks with microdermabrasion
Vakuum microdermabrasion with aluminium oxide microcrystals is long lasting and takes a long time (each stretch mark is polished lengthwise (Fig.4)). Vacuum microdermabrasion can be successfully used for both red and white stretch marks on all body areas. It is moderately painful. It requires about 4-8 treatments at 3-4 week intervals.
Fig.4. Stretch marks treatment on thighs with microdermabrasion
Can stretch marks be removed with a peeling?
A glycolic acid peeling for stretch marks with 50-70% AHA is usually performed after a month of preparation. Before the AHA peeling treatment, a cream containing tretinoin or glycolic acid is applied for one month. However, even after the preparation, the results are unsatisfactory. TCA peelings penetrate deeper than AHA ones and therefore give better results (Fig.8). TCA peeling gives the best results when treating fresh stretch marks on the chest, abdomen, thighs, hips and buttocks.
Stretch marks treatment with laser?
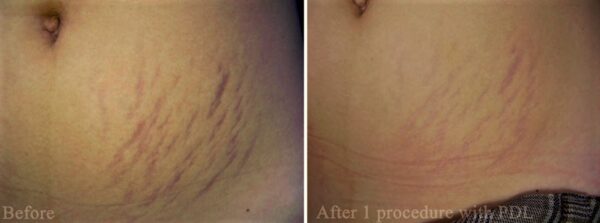
An ablative laser vaporizes the epidermis and part of the dermis to smooth the skin surface. The effect of this laser treatment of stretch marks is negligible and the side effects are much more severe than the expected results. The non-ablative laser (PDL) is effective in treating red stretch marks on the buttocks, breasts, abdomen, hips and thighs (Fig. 5). It can remove the redness (blood vessels) inside the stretch marks, but the stretch marks on the skin remain unaffected.
Fig.5. Treatment of stretch marks with laser
Is it possible to get rid of stretch marks with a cream?
It should be said straight away that creams can only improve fresh (red) stretch marks. You cannot even try to improve old (white) stretch marks with creams alone. This is impossible and leads to a waste of money.
But what is the best cream to remove fresh stretch marks? Today, there are plenty of creams on offer to prevent the appearance of stretch marks during pregnancy. These include Skinception, Cicamed scar ointment, Remescar stretch mark cream etc…
But is it really so?
Firstly, the appearance of stretch marks is a genetic problem. There is no cream that can change the structure of the genome. Therefore, there is not and cannot be a cream that prevents stretch marks.
Secondly, most of the stretch mark gels and creams are silicone-based and have a positive effect in the treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloids. However, hypertrophic scars and stretch marks are not the same thing. The cream used to treat keloids and hypertrophic scars cannot be the same cream used to remove stretch marks or atrophic scars.
What methods do we use for stretch marks treatment and correction?
These are:
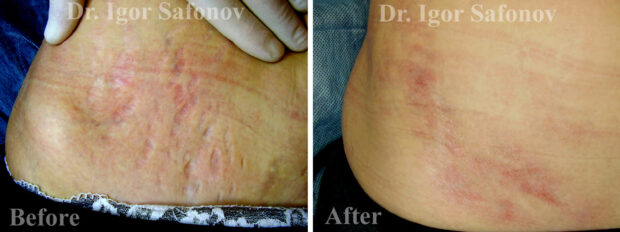
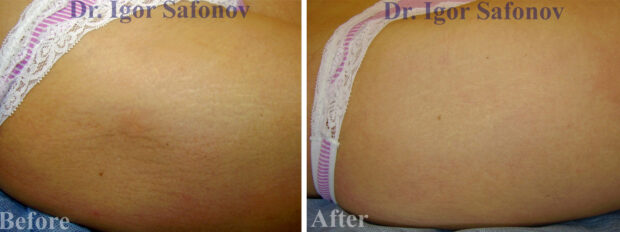
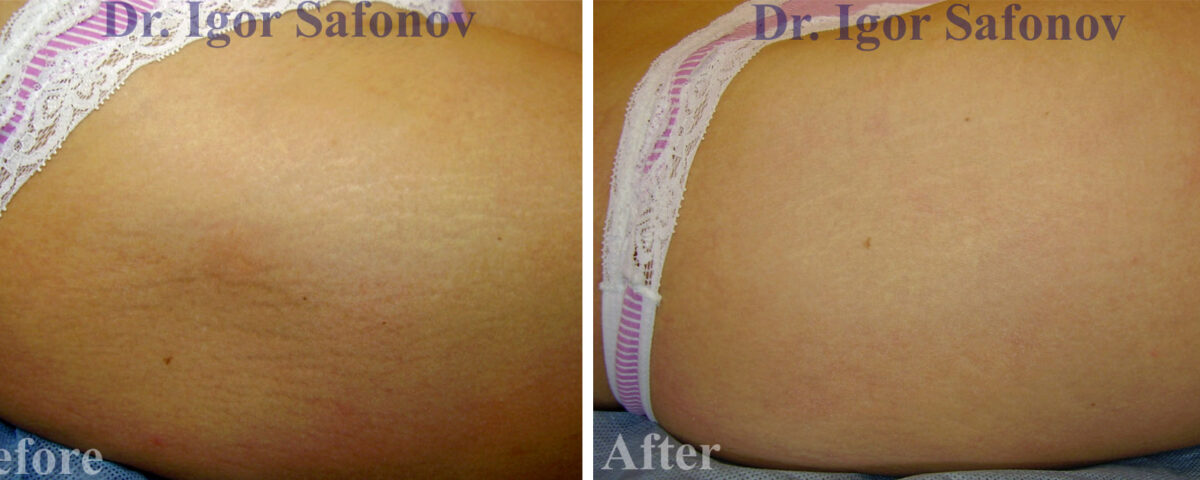
- Combined method against stretch marks with sand scraping, TCA peeling and alternating occlusion. The method is quick (the procedure takes 40-60 minutes) and practically painless. There is no set number of treatments. Results are evaluated in 8-12 weeks after each treatment and when the result is considered satisfactory (usually 1-2 treatments 2-3 months apart), the treatment is terminated.
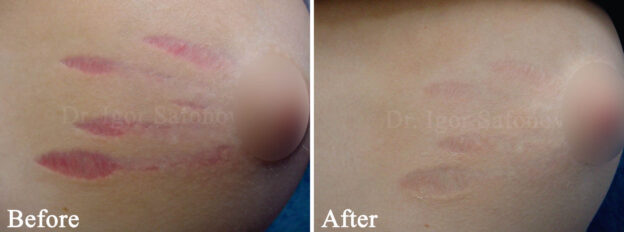
- Microneedling treatment for stretch marks. Stretch marks can be treated with microneedling (dermapen, dermaroller, dermapen). Microneedles of 1.0-1.5 mm in length form a large number of microchannels in the skin with a diameter of 0.08 mm. The damaged cells in the treated area start to divide intensively and produce collagen to regenerate the skin defect. The collagen islands formed in the channels are attracted to each other and reduce the distance between the edges of the tear.
Fig.6. Elimination of stretch marks on the buttocks with microneedling (dermaroller / skin roller / dermapen)
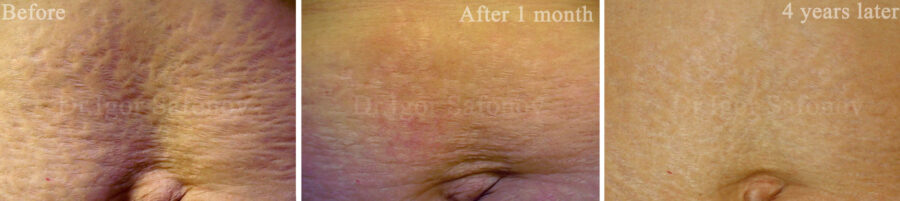
Stretch marks removal before and after
Note! Unfortunately, there is no method to prevent stretch marks! But the sooner you start treating stretch marks, the better results you can expect!