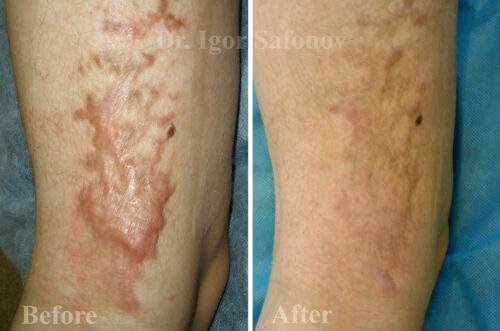
KELOIDS and HYPERTROPHIC SCARS Treatment and Correction
In the treatment, removal and correction of keloids and hypertrophic scars the following methods and techniques are used with various successes: pressure therapy, silicone sheetings, surgery, laser treatment, intralesional corticosteroids injections, cryotherapy or cryosurgery, radiotherapy, microneedling.
Keloids (keloid scars) as well as hypertrophic scars can be difficult to treat. Keloids that underwent surgery or laser treatment are especially resistant to all types of treatment.
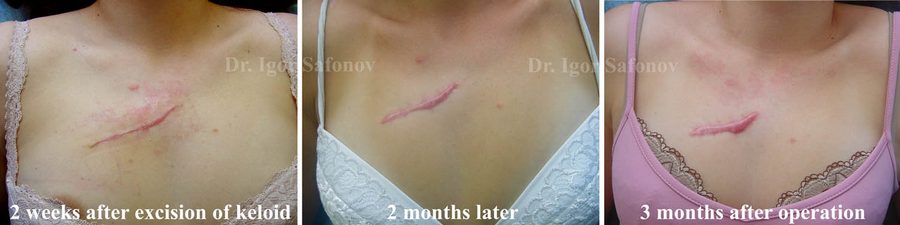
Surgical excision of keloid
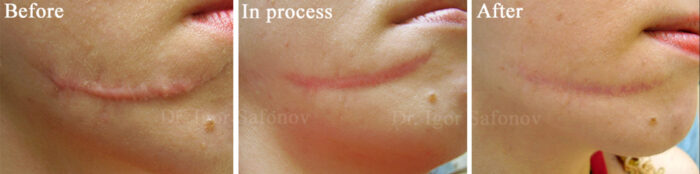
Surgical excision of keloid as an independent method results in 95-100% recurrence (Fig.1.) Therefore surgical removal of keloid cannot be applied without combinations with other methods. Surgical excision produces an acceptable result in treating hypertrophic scars.
Radiotherapy of keloid (X-ray therapy)
Radiotherapy of keloid has very disputed effects. The method results in 50-100% relapse of keloids when applied as the only method. Superficial X-rays have been employed primarily as an adjunct to surgical removal of keloids. Radiotherapy of keloid should be started as early as possible (in the first 24 hours) after keloid excision. A total dose of usually 12 – 15 Gy is divided to 6-7 times (is recommended every second day). Side effects include hypo- and hyper-pigmentation, erythema, telangiectasia, post-radiation fibrosis and skin atrophy. Carcinogenicity is not proven, but the method is rarely used and only in combination with other methods. Radiotherapy of keloid is not used in children, in hair regions of the head, thyroid, face and breasts in women.
Pressure therapy for keloid and hypertrophic scars (Compression therapy)
Compression therapy or pressure therapy are effective for prevention of hypertrophic scars and treatment of keloids.
The continuous compression of 20-40 mm of mercury is applied for 12-24 hours per day in course of 3-12 months. On the one hand, it resists the scar tissue growth, holding it mechanically within limited space. On the other, by putting pressure on the scar vessels blocks its nutrition, specifically decreased oxygen supply to the scar tissue, which results in termination of its growth or partial regression. Pressure therapy is usually performed with pressure dressings or bandages, masks and gloves.
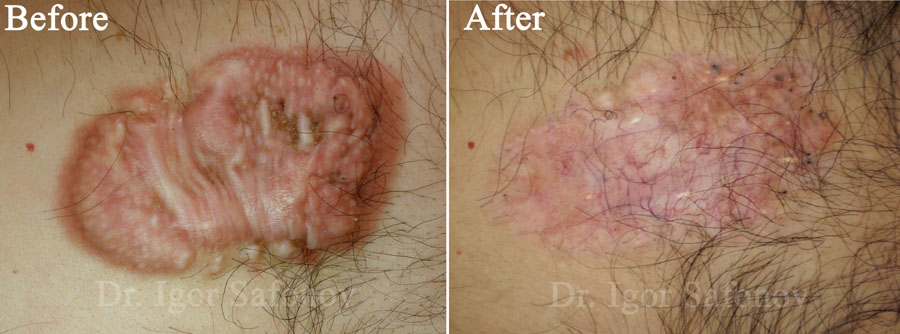
Silicone based products (silicone gel, silicone sheeting)
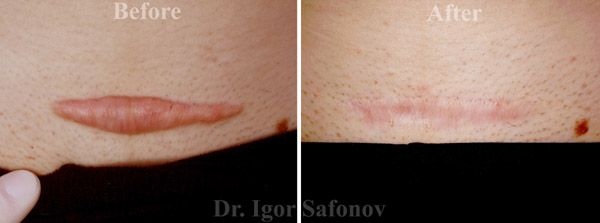
Mechanism of action of silicone sheeting for the treatment of hypertrophic scars and keloid is not been fully cleared. There are two points of view about it. The first opinion suggests that silicone sheeting normalize the transepidermal water loss and hydrate the scar. Another opinion suggests that silicone sheeting compress capillaries, block the delivery of inflammatory mediators, and reduce collagen synthesis due to local ischemia (Fig. 2). Silicone sheets are usually being employed 12–24 hours per day over a period of 6–12 months beginning 2 weeks after wounding.
Creams and gels for keloid and hypertrophic scars
Laser treatment for keloids
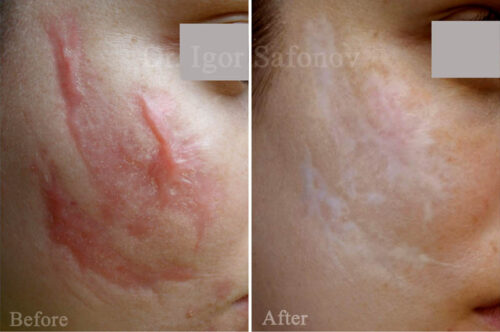
Ablative lasers produce a high relapse rate (90-100%) when applied in hypertrophic scars and keloids treatment. Clinical efficacy with vascular laser (non-ablative) applied in hypertrophic scars treatment constitutes 75-95%, keloids – 60-70%. Primary task of laser treatment is to block in the keloid scar blood vessels that provide scar nutrition.
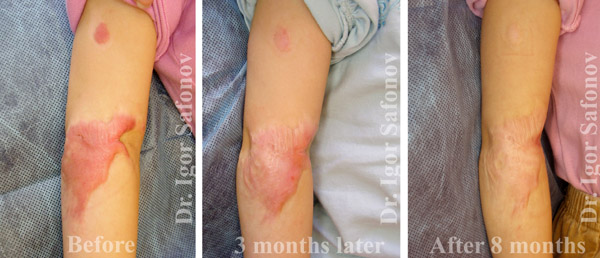
Fig.4. Hypertrophic scars treatment with laser and cryotherapy. Post injury scars before and after treatment
Intralesional steroid injection for keloids
Steroid are administered locally (to prevent keloid formation) by intralesional injections of triamcinolone acetonide injection (Kenalog crystalline suspension) to treat active keloids and old hypertrophic scars. Intralesional corticosteroid injections reduce collagen synthesis not only by inhibiting fibroblast mitosis (cells synthesizing collagen), but along with collagenase (collagen-resolving enzyme) concentration increase. Besides, steroids possess a strong anti-inflammatory action.
Cryosurgery or cryotherapy for keloids and hypertrophic scars
Mechanism of tissue damage by cryotherapy or cryosurgery using cryogen is conditioned by affection of microvasculature, destruction of cytoplasm and cell organelles caused by intracellular and intravascular formation of ice crystals. Concentration of electrolytes in cells is increased when thawing, accompanied by greater crystallization after repeated freezing which accelerates their destruction. When applied as a monomethod, cryotherapy results in complete elimination of keloids and hypertrophic scars with 51 and 74% relapse-free of cases, correspondingly.
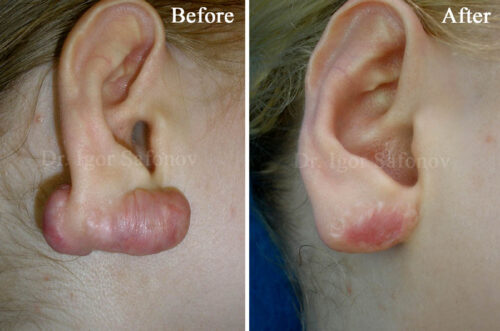
The combination of cryotherapy or cryosurgery with other techniques much more efficient and provides positive results in 76-90% after 30 month follow-up period. (Dr. Igor Safonov: Cryotherapy of ear keloid).
Microneedling (dermapen, dermaroller) for keloids and hypertrophic scars
Microneedling for keloids and hypertrophic scars can be applied in any regions of human body. Collagen fibers in keloids are located differently compared to regular scars. They are located relatively in parallel to the skin surface in the normotrophic scars (Fig.7) and chaotically and node-like, resembling a fingerprint in keloids (Fig.8).
To improve the appearance of these inactive scars and reduce their height, it is necessary to destroy these chaotically located collagen fibers. In these places, new fibers are created, which are parallel to the skin surface. This can be performed using microneedling with dermaroller or dermapen (Fig.9).
Microneedles penetrate into the dermis and destroy the coarse collagen fibers. The more punctures, the more collagen fibers are destroyed. New collagen fibers formed at the punctures, are parallel to the skin surface. This leads to a reduction in the size of the scar and an improvement in its elasticity.
Microneedles of dermapen or dermaroller penetrate into the skin up to the mesoderm and mechanically destroy the scar tissue fibres (Fig.9). In this case, depending on the thickness, prescription and location of the scar microneedling with the length of needles from 0.5 mm to 2.5 mm are used.

![[:en]Collagen fibers of a normotrophic scar [:ru]normal_scar[:sv]normal_scar[:de]normal_scar[:]](https://scarshelper.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/normal_scar-1.jpg)
![[:en]Collagen fibers of keloid[:ru]keloidl_scar[:sv]keloidl_scar[:de]keloidl_scar[:]](https://scarshelper.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/keloidl_scar.jpg)
![[:en]Microneedling for pathological scar. Scheme[:ru]img.4_7[:sv]img.4_7[:de]img.4_7[:]](https://scarshelper.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/img.4_7.jpg)